Maps of Somerset England
Home > Maps of England > Somerset Maps
Welcome to our Somerset map page. The map of Somerset England that is located below is provided by Google Maps. You can "grab" the electronic map and move it around to re-center the map. You can change between standard map view and satellite map view by clicking the small square on the bottom left-hand corner of the map. Satellite map view utilises orbiting satellite and / or aerial high-resolution photography to display images of the map location to street level detail (really quite amazing). Standard map view shows a traditional street map (also known as a road map). You can use the zoom buttons on the bottom right-hand side of the map to zoom in or out to street level detail. We have digital online maps for most towns and cities on the Maps of England page. We also have a good collection of old school printable maps on the Maps of England page.
A map of Somerset, England
Somerset Maps
I hope you like the Somerset County, England street map / road map situated above.
If you like our website, please consider adding a link to the site. These links help to build website traffic and they are considered a vote of confidence for a site.
Somerset
Somerset is a county in South West England which borders Gloucestershire and Bristol to the north, Wiltshire to the east, Dorset to the south-east and Devon to the south-west. It is bounded to the north and west by the Severn Estuary and the Bristol Channel, its coastline facing southeastern Wales. Its traditional border with Gloucestershire is the River Avon. Somerset's county town is Taunton.
Somerset is a rural county of rolling hills, the Blackdown Hills, Mendip Hills, Quantock Hills and Exmoor National Park, and large flat expanses of land including the Somerset Levels. There is evidence of human occupation from Paleolithic times, and of subsequent settlement by the Celts, Romans and Anglo-Saxons. The county played a significant part in Alfred the Great's rise to power, and later the English Civil War and the Monmouth Rebellion. The city of Bath is famous for its Georgian architecture and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
History
The caves of the Mendip Hills were settled during the Palaeolithic period, and contain extensive archaeological sites such as those at Cheddar Gorge. Bones from Gough's Cave have been dated to 12,000 BC, and a complete skeleton, known as Cheddar Man, dates from 7150 BC. Examples of cave art have been found in Aveline's Hole. Some caves continued to be occupied until modern times, including Wookey Hole.
The Somerset Levels-specifically dry points at Glastonbury and Brent Knoll- also have a long history of settlement, and are known to have been settled by Mesolithic hunters. Travel in the area was facilitated by the construction of one of the world's oldest known engineered roadways, the Sweet Track, which dates from 3807 BC or 3806 BC.
The exact age of the henge monument at Stanton Drew stone circles is unknown, but it is believed to be Neolithic. There are numerous Iron Age hill forts, some of which, like Cadbury Castle and Ham Hill, were later reoccupied in the Early Middle Ages.
On the authority of the future emperor Vespasian, as part of the ongoing expansion of the Roman presence in Britain, the Second Legion Augusta invaded Somerset from the south-east in AD 47. The county remained part of the Roman Empire until around AD 409, when the Roman occupation of Britain came to an end. A variety of Roman remains have been found, including Pagans Hill Roman temple in Chew Stoke, Low Ham Roman Villa and the Roman Baths that gave their name to the city of Bath.
After the Romans left, Britain was invaded by Anglo-Saxon peoples. By AD 600 they had established control over much of what is now England, but Somerset was still in native British hands. The British held back Saxon advance into the south-west for some time longer, but by the early eighth century King Ine of Wessex had pushed the boundaries of the West Saxon kingdom far enough west to include Somerset. The Saxon royal palace in Cheddar was used several times in the 10th century to host the Witenagemot.
The nature of the relations between the Britons and the Saxons in Somerset is not entirely clear. Ine's laws demonstrate that the Britons were considered to be a significant enough population in Wessex to merit provisions; however, the laws also suggest that Britons could not attain the same social standing as the Saxons, and that many were enslaved. In light of such policies, many Britons might have chosen to emigrate to places such as Brittany while those who remained would have had incentives to adopt Anglo-Saxon culture.
After the Norman Conquest, the county was divided into 700 fiefs, and large areas were owned by the crown, with fortifications such as Dunster Castle used for control and defence. Somerset contains HM Prison Shepton Mallet, which was England's oldest prison still in use prior to its closure in 2013, having opened in 1610. In the English Civil War Somerset was largely Parliamentarian, with key engagements being the Sieges of Taunton and the Battle of Langport.
In 1685 the Monmouth Rebellion was played out in Somerset and neighbouring Dorset. The rebels landed at Lyme Regis and travelled north, hoping to capture Bristol and Bath, but they were defeated in the Battle of Sedgemoor at Westonzoyland, the last pitched battle fought in England. Arthur Wellesley took his title, Duke of Wellington from the town of Wellington; he is commemorated on a nearby hill by a large, spotlit obelisk, known as the Wellington Monument.
The Industrial Revolution in the Midlands and Northern England spelled the end for most of Somerset's cottage industries. Farming continued to flourish, and the Bath and West of England Society for the Encouragement of Agriculture, Arts, Manufactures and Commerce was founded in 1777 to improve farming methods. Despite this, 20 years later John Billingsley conducted a survey of the county's agriculture in 1795 and found that agricultural methods could still be improved. Coal mining was an important industry in north Somerset during the 18th and 19th centuries, and by 1800 it was prominent in Radstock.
The Somerset Coalfield reached its peak production by the 1920s. All the pits have now been closed, the last in 1973. Most of the surface buildings have been removed, and apart from a winding wheel outside Radstock Museum, little evidence of their former existence remains. Further west, the Brendon Hills were mined for iron ore in the late 19th century; this was taken by the West Somerset Mineral Railway to Watchet Harbour for shipment to the furnaces at Ebbw Vale.
Many Somerset soldiers died during the First World War, with the Somerset Light Infantry suffering nearly 5,000 casualties. War memorials were put up in most of the county's towns and villages; only nine, described as the Thankful Villages, had none of their residents killed. During the Second World War the county was a base for troops preparing for the D-Day landings. Some of the hospitals which were built for the casualties of the war remain in use. The Taunton Stop Line was set up to repel a potential German invasion. The remains of its pill boxes can still be seen along the coast, and south through Ilminster and Chard.
A number of decoy towns were constructed in Somerset in World War II to protect Bristol and other towns. They were designed to mimic the nighttime geometry of "blacked out" streets, railway lines, and Bristol Temple Meads railway station, to encourage German bombers away from these targets. One, on the German radio navigation beam flight path to Bristol, was constructed on Beacon Batch. It was laid out by Shepperton Studios, based on aerial photographs of the city's railway marshalling yards. The decoys were fitted with dim red lights, simulating activities such as the stoking of steam locomotives. Burning bales of straw soaked in creosote were used to simulate the effects of incendiary bombs dropped by the first wave of Pathfinder night bombers; meanwhile, incendiary bombs dropped on the correct location were quickly smothered, wherever possible. Drums of oil were also ignited to simulate the effect of a blazing city or town, with the aim of fooling subsequent waves of bombers into dropping their bombs on the wrong location. The Chew Magna decoy town was hit by half a dozen bombs on 2 December 1940, and over a thousand incendiaries on 3 January 1941. The following night the Uphill decoy town, protecting the airfield at Weston-super-Mare, was bombed; a herd of dairy cows was hit, killing some and severely injuring others.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
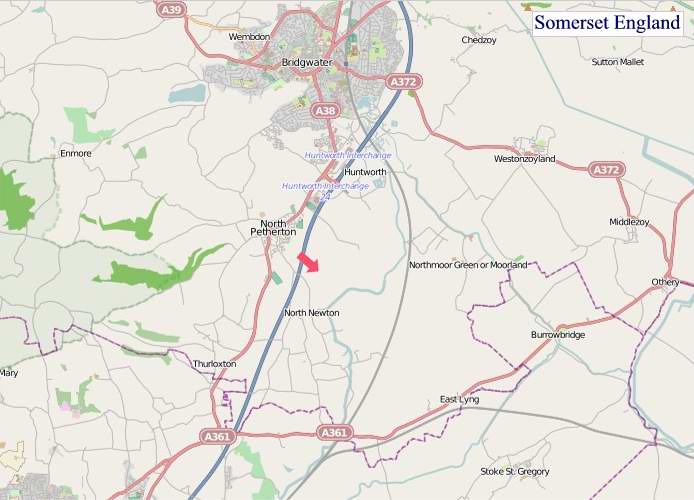
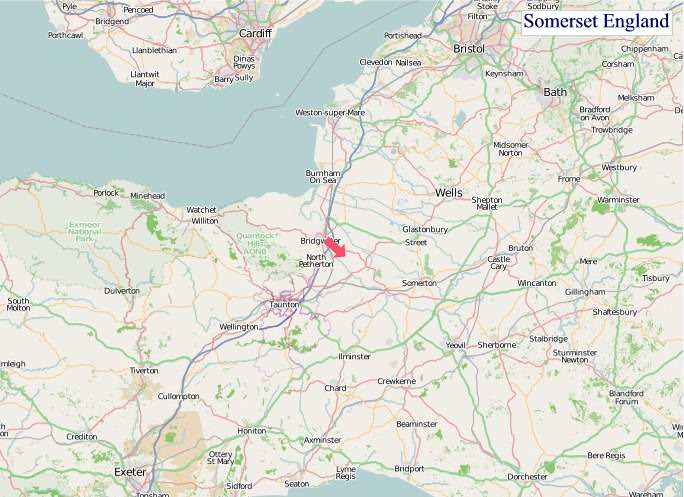
"© OpenStreetMap contributors, CC BY-SA".
Districts of Somerset
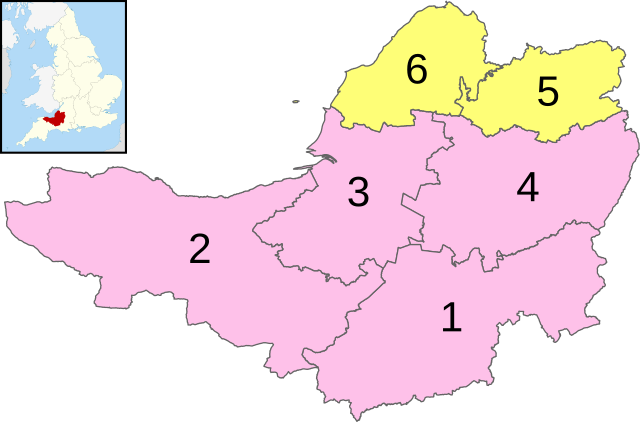
1 - South Somerset
2 - Somerset West and Taunton
3 - Sedgemoor
4 - Mendip
5 - Bath and North East Somerset (Unitary)
6 - North Somerset (Unitary)
Music


